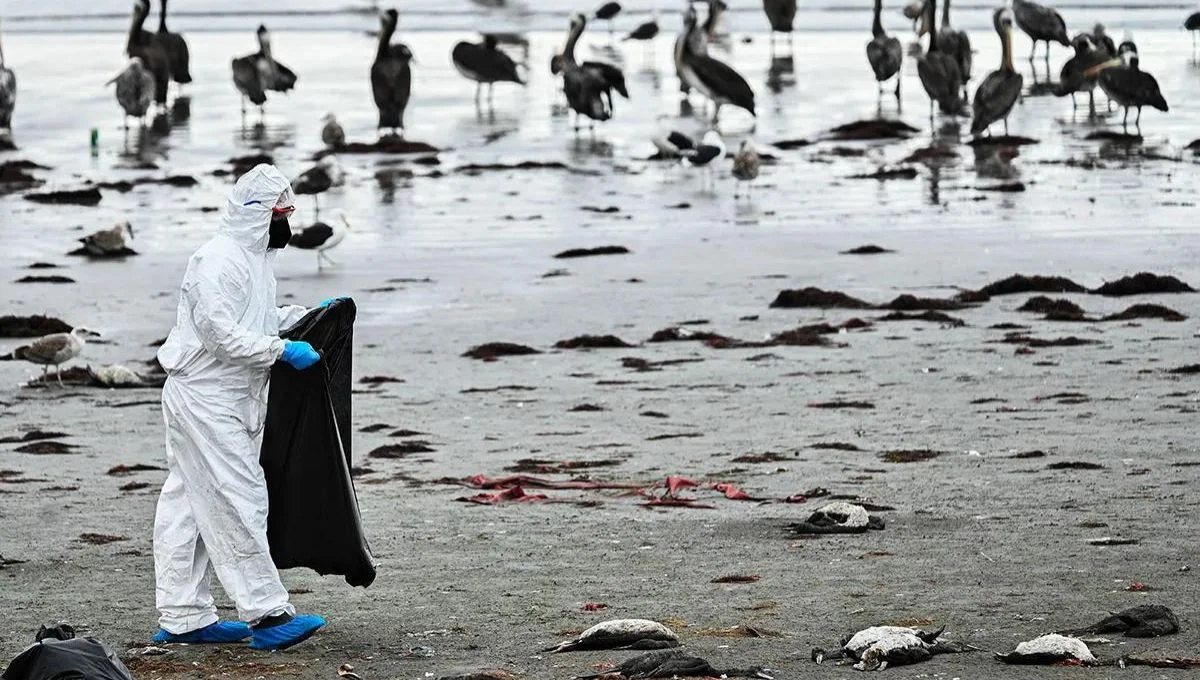
Here we will tell you that “why does bird flu occur every year in America“, Bird flu, or avian influenza, recurs annually in America due to several factors:

- Migration of Wild Birds: Many types of avian influenza are spread by wild migratory birds, especially waterfowl. These birds travel long distances and can spread the virus to various regions, including the United States, during their migration patterns.
- Poultry Farms: The US has a large poultry industry with densely populated farms. Once the virus enters a farm, it can spread rapidly among birds due to close quarters and shared resources
- Environmental Factors: The virus can survive in certain environments, such as in water or on surfaces contaminated with bird droppings. This allows the virus to persist and spread, particularly in areas with large populations of wild birds or near water sources.
- Biosecurity Lapses: Despite efforts to maintain strict biosecurity measures, lapses may occur, allowing the virus to enter and spread in poultry farms.
- Human Activities: The movement of birds (both wild and domestic), poultry products and equipment can contribute to the spread of the virus. Farmers, workers and equipment moving between farms may inadvertently transfer the virus.
- Mutations and Variants: Avian influenza viruses can mutate, producing new variants that may spread more easily or be harder to control. These mutations can help the virus persist and adapt to different hosts and environments.
Preventive measures, including enhanced biosecurity, monitoring of wild bird populations, and rapid response to outbreaks, are critical to managing and mitigating the impact of bird flu in the U.S. and globally.
What are the potential risks of bird flu mutations leading to a pandemic?
The potential risks of a bird flu mutation causing a pandemic are significant and multifaceted. Here are some key points to consider:
Increased human-to-human transmission
Genetic recombination: If an avian influenza virus mixes with a human influenza virus within a host (such as a pig), the resulting virus may gain the ability to transmit easily between humans.
Mutations: Even without recombination, mutations in the virus can increase its ability to infect humans and spread from person-to-person.
Lack of immunity

New virus strains: If a new, highly infectious strain emerges, humans will likely have little or no pre-existing immunity, leading to rapid and widespread infection.
Limited vaccine availability: It can take months to develop and distribute a new vaccine for a new strain, leaving the population vulnerable in the interim period.
Serious health effects:
High mortality: Some strains of avian influenza, such as H5N1, have a high mortality rate in humans. Epidemics can result in large numbers of deaths.
Severe illness: Even non-fatal cases can cause severe respiratory illness, increasing the burden on the healthcare system.
how to prevent bird flu ?
Preventing bird flu involves a combination of biosecurity measures, surveillance, and public awareness. Here are the main strategies to prevent bird flu:
Biosecurity measures on poultry farms
Restrict access: Restrict access to poultry farms to only essential personnel. Implement strict control measures for visitors and vehicles.
Clean equipment: Regularly disinfect equipment, clothing, and vehicles that come into contact with poultry.
Separate species: Keep different species of birds separate to reduce the risk of cross-species transmission.
Control access to wild birds: Prevent wild birds from coming into contact with domestic poultry by using netting or indoor housing.
Safe feed and water: Ensure that feed and water sources are not contaminated by wild birds or rodents.
Surveillance and monitoring
Regular health checks: Perform regular health checks on poultry to detect early signs of disease.
Testing: Implement regular testing of birds for avian influenza, especially in areas with a high risk or history of outbreaks.
Reporting systems: Establish efficient systems to report suspected cases of bird flu to authorities.
Vaccination and treatment
Vaccination programs: In some areas, authorities may implement vaccination programs for poultry to prevent infection.
Antiviral medications: Use antiviral medications as directed by veterinary professionals in case of an outbreak.
Hygiene and cleanliness
Hand washing: Ensure that all farm workers wash their hands thoroughly before and after handling birds.
Protective gear: Use protective clothing, gloves, and masks when handling birds, especially if there are sick birds.
Public awareness and education
Training: Provide training to farmers and workers on the importance of biosecurity measures and how to implement them.
Awareness campaigns: Conduct public awareness campaigns about the risks of bird flu and how to prevent it.
Controlling the movement of birds
Limit the movement of birds: Restrict the movement of birds and eggs between farms and areas, especially during outbreaks.
Quarantine: Quarantine new birds before introducing them into the existing flock to ensure they are disease-free.
Environmental control
Rodent control: Implement rodent control measures to prevent the virus from spreading.
Proper disposal: Ensure proper disposal of dead birds and waste material to prevent contamination.
International cooperation
Information sharing: Share information and best practices with international bodies and neighbouring countries to prevent the spread of avian influenza.
Compliance with trade regulations: Follow international trade regulations and guidelines to prevent the spread of avian influenza through poultry trade.
Personal protection
Avoid contact with wild birds: Avoid direct contact with wild birds, especially in areas where avian influenza outbreaks occur.
Cook poultry thoroughly: Ensure poultry and eggs are cooked thoroughly to eliminate potential viruses.
Implementing these measures can greatly reduce the risk of a bird flu outbreak and protect both animal and human health.
